Defence and Security
At
a seminar organised by the Defence Research and Development Organisation
(DRDO), Defence Minister encouraged scientists to work towards developing
hypersonic missile technology.
·
History of missile
technology in india – Before Independence, many kingdoms in india were using
rockets as a part of their warfare technologies. Mysore ruler Hyder Ali started
inducting iron-cased rockets in his army within the mid-18th century.
·
By the time Hyder’s son
tipu sultan died, an organization of rocketeers was connected to every brigade
of his army, that has been estimated at around 5,000 rocket-carrying troops.
·
At the time of
Independence, Asian nation didnt have any indigenous missile capabilities.
·
The government created
the Special Weapon Development Team in 1958.
·
This was later expanded
and known as the Defence analysis and Development Laboratory (DRDL), that moved
from delhi to Hyderabad by 1962.
·
In 1972, Project Devil,
for the development of a medium range Surface-to-Surface Missile was initiated.
·
A large number of
infrastructure and test facilities were established throughout this period.
·
By 1982, DRDL was
performing on many missile technologies under the Integrated guided Missiles Development Programme (IGMDP).
What kind of missiles
does India have?
·
India is considered among the highest few nations once it comes to
designing and developing missiles indigenously, though its method behind the
United States, China and Russia in terms of range. Among the surface-launched
systems
·
ANTI-TANK
guided MISSILE: Nag has already been inducted into the services. Nag
is that the only “fire-andforget ATGM meeting all weather needs for its range
(around twenty km)”. Recently Heli-Nag was tested, which can be operated from
helicopters and can be inducted by 2022. theres also a Stand-off Anti-Tank
(SANT) missile, with a variety over ten kilometer.
·
SURFACE-TO-AIR
MISSILE: The
short-range surface-to-air missile system Akash has already been inducted within
the Army and also the Air Force. For Akash one, that has a seeker, which
enhances target detection in all climatic conditions, the military has already
got the Acceptance of nacessarity from the govt.. For Akash (New Generation),
the 1st tests were conducted in July this year.
·
MEDIUM-RANGE
SAM: Production of
MRSAM systems for the Navy is complete, and its placing its order. The
Jaisalmer-based 2204 Squadron of the Air Force became the 1st unit to get the
MRSAM systems in Sept this year. Technology for MRSAM for the military “is
conjointly during a good shape and can be flight-tested soon”.
·
SHORT-RANGE
SAM: For the Navy,
the 1st flight tests are with success conducted. many air-launched systems –
air-to-air Astra, India’s beyond visual range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM), has
been fully tested and is under induction. its a variety of around one hundred
kilometer. A long-range Astra is additionally being developed, that initial
tests have been conducted. The missile uses solid fuel ramjet technology, which
enhances speed, and can have an indigenously-built seeker.
·
AIR-TO-GROUND: Rudram, a new Generation Anti-Radiation Missile
(NGRAM), has cleared initial tests. With a maximum range of around two hundred
kilometre, the missile in the main targets communication, radar and
surveillance systems of the adversary. BrahMos, that india developed conjointly
with Russia, is already operational. its a three hundred kilometre to five
hundred kilometre range, and may be a short-range, ramjet-powered, single
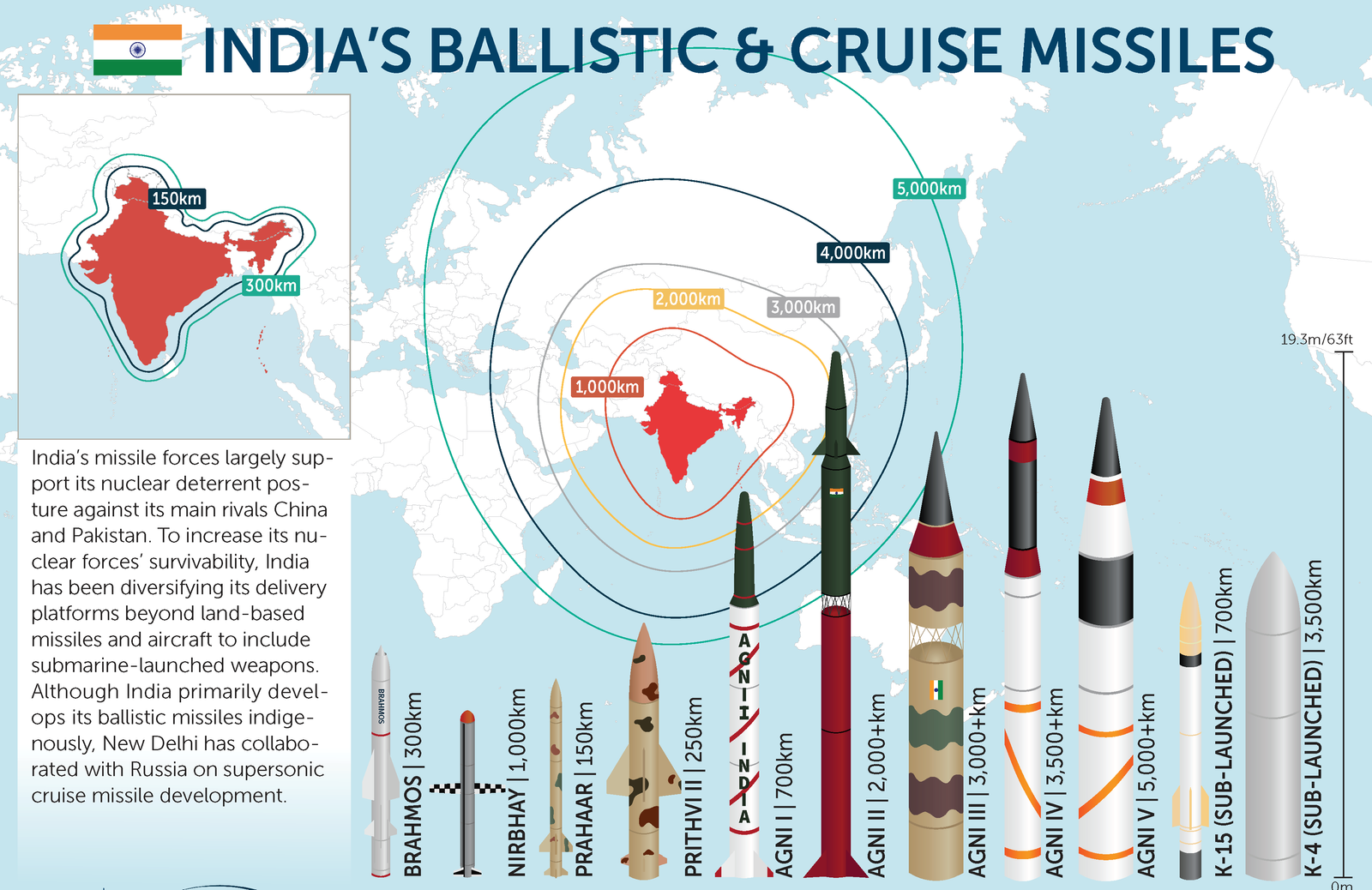
warhead, supersonic anti-ship or land attack cruise missile. Which of India’s
missile systems are most important? the 2 most important are agni and Prithvi,
each getting used by the Strategic Forces Command. agni (range around 5,000 ) ,
is India’s solely contender for an inter-continental ballistic missile (ICBM),
that is available with solely a few countries. Prithvi, though a short-range
surface-to-surface missile with a 350 kilometre range, has strategic uses.
india conjointly tested a anti-satellite system in Apr 2019. A changed
anti-ballistic missile named Prithvi Defence Vehicle Mk two was used to hit a
low-orbit satellite. It put india only behind the United States, Russia and
China during this capability. Hypersonic technology india has been performing
on this for some years, and is simply behind the United States, Russia and
China. DRDO with success tested a Hypersonic Technology demonstrated Vehicle
(HSTDV) in Sept 2020, and demonstrated its hypersonic air-breathing scramjet
technology. According to sources, india has developed its own cryogenic engine and in
a it during a 23-second flight. india can try and create a hypersonic cruise
missile, using HSTDV. Sources said solely Russia has proved its hypersonic missile capability thus far,
whereas China has demonstrated its HGV capability. india is expected to be
ready to have a hypersonic weapons system among four years, with medium- to
long-range capabilities. wherever do China stand compared to india? China is
ahead of India. According to a Pentagon report in 2020, China might
have either achieved parity, or maybe exceeded the United States in land-based
conventional ballistic and cruise missile capabilities. India’s solely nuclear
missiles are Prithvi and agni, however far off those, tactical nuclear weapons
may be fired from some IAF fighter jets or from Army guns, that have a low
range, around fifty kilometre.

Comments